Functionality
Focusing on service
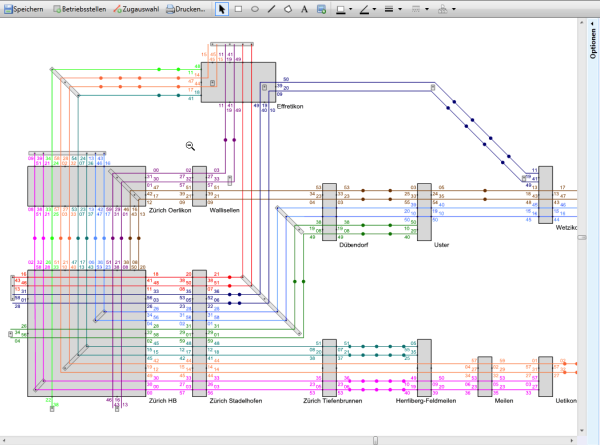
Netgraph
The introduction of coordinated (“interval”) timetables has led to the ability to represent timetables in a way that shows both the geographical network and the train times in an efficient manner on a “netgraph”. A single line represents each service (and the corresponding journey in the reverse direction) connecting the stations it passes through on its trip, with the arrival and departure times for each station indicated. The cyclical aspect of the timetable means that a whole repeating family of trains can be covered by one line on the diagram.
The connection times between services at a station can be seen at a glance, giving a powerful method for improving the coordination between services for the train planner.
Viriato was the first planning tool to successfully combine this netgraph with graphic and tabular timetables to produce a single integrated planning tool.
Visualise capacity
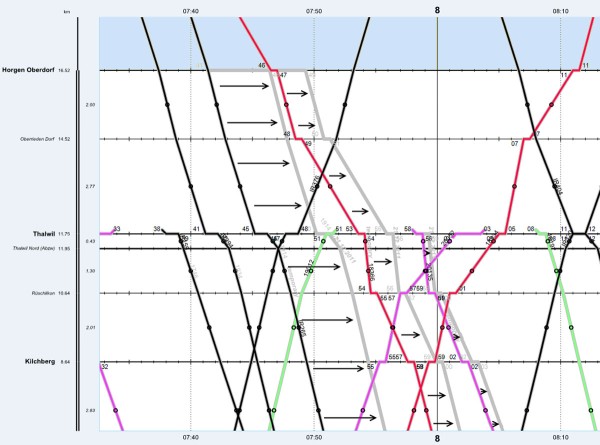
Graphic timetable
Graphic timetables represent train operations and are pivotal when determining the interactions between trains at a network-wide level. Graphic timetables can also be used to identify the likely rolling stock requirements for a line and produce initial utilisation plans.
An experienced timetable planner can assess the feasibility of a timetable and the plan, such as insufficient headways between services or conflicting movements over a single track section simply by looking at a graphic timetable
Viriato’s highly configurable graphic timetable functionality allows users to represent the trains according to their needs. For example, colours may indicate different train types (e.g. by service group or line), while line thickness may reflect express or regional service. Such customisation gives timetable planners the power to produce highly descriptive graphical timetables, and to identify timetable improvements.
Production facts and figures
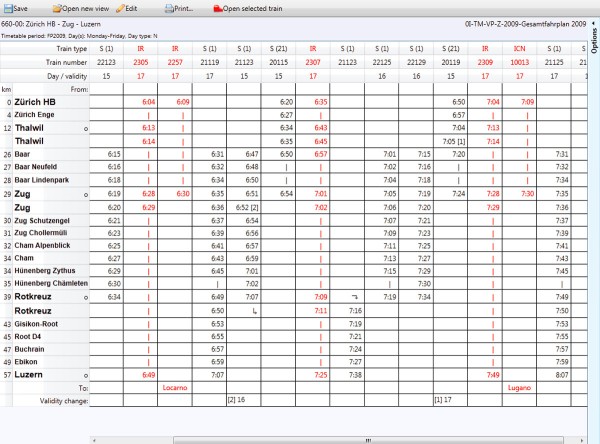
Customer Timetable
Timetables form a clear description of the service in terms of product type, coverage, frequency and/ or station calling pattern policy, and are thus indispensable.
The customer timetable is the traditional method for presenting the schedule of trains along a route. The functional requirements for a customer timetable vary depending on how it will be used. Used in conjunction with the operational modules, such as the graphic timetable, it provides further insights into aspects of the timetable on rail traffic.
Viriato provides flexible filter possibilities and layout settings that permit users to easily display the desired information. Viriato also provides an interface that allows customer timetable data to be analysed and/or displayed using MS Excel.
The connection clock shows graphically the relationship between arriving and departing services at a station so that the timetable planner can efficiently manage the arrival and departure times. This maximises the connection possibilities for customers so that as many potential journey combinations as possible become practical for travellers. The arrival and departure times of services are shown in the form of a clock arranged around the node allowing this information to be absorbed in a glance. The user can also display the usage of specific platforms during the hour.
Every day is not like Sunday
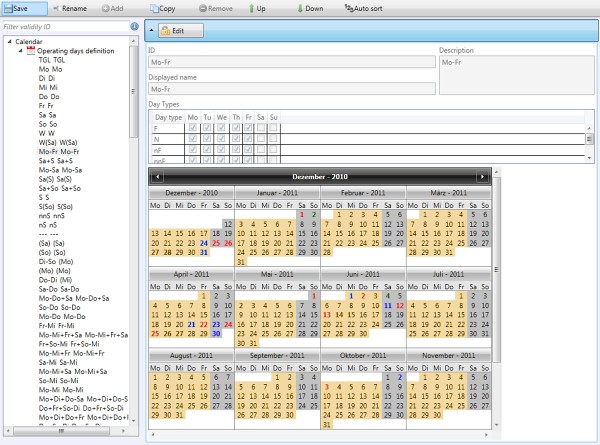
Calendar
At the conceptual planning level a nominal day can be used to develop and evaluate timetables; however, as the date of timetable introduction draws near, planners must define the timetable in greater detail to include weekend variations, holidays and other service pattern alterations. Actual operations require day-specific timetables to allow responses to shortterm changes, such as additional or cancelled trains, to be incorporated in the working plan.
To incorporate this flexibility, Viriato has a train specific validity model allowing the timetable planner to assign any operating pattern to a chosen train, even allowing different validities to trains within a train family. To help manage this process, Viriato allows the definition of template validities that can be assigned to trains. Naturally these can be modified later on a train-specific basis. Viriato generates validity descriptions allowing the user to see at a glance when a train operates.
For the efficient management of train validities within a timetable, the user can modify the running days of multiple selected trains using a bulk update option.
All output views allow the user to filter by days and dates which trains are displayed.
Switzerland’s official running times supplier
Running time calculator
Accurate train planning requires a detailed knowledge of a train’s technically feasible running time. The ability to dynamically recalculate the running time during the planning process is essential. This allows changes in rolling stock and infrastructure, such as temporary speed restrictions for engineering works, to be included in the timetable. Viriato makes it possible to calculate precise running times based on a wide range of technical and operational parameters.
The running time calculator in Viriato includes the algorithm used by Swiss Federal Railways (SBB) and by Infrabel to calculate all their running times in Switzerland and Belgium. This calculator allows an unlimited combination of rolling stock types, traction values, dynamic resistances and braking curves to produce highly accurate running times which have been validated by SBB during their daily operations.
The civil engineering characteristics of the infrastructure such as gradients, curvature and speed restrictions are entered to produce a highly detailed model of the railway.
The Viriato running time calculator allows users to easily define their own rolling stock types with associated performance characteristics.
The Viriato running time calculator integrates fully into the train planning process, and the results are instantly reflected in a train’s running times.
Round and round they go
Vehicle rostering
The Viriato Vehicle Rostering module is fully integrated with the timetabling functionality of Viriato, allowing the creation of vehicle rosters during the planning process.
Throughout the life cycle of a timetable there are different requirements for vehicle rostering, and the Viriato Vehicle Rostering module provides the functionality for this entire process.
- The vehicle rostering process is fully integrated with the timetable. If running times or routes are changed, this is reflected in the vehicle roster too. User definable tolerances allow the planner to decide what level of change is allowed before a revised roster is required.
- The vehicle rosters can be created and managed in several different types of Gantt-chart type views. The compact view compresses a time period into a single day allowing the planner to quickly see which activities link consistently and which occur less frequently. A rolled-out view shows the roster in a continuous day-by-day format allowing the links to be traced through the plan. Finally, a vehicle specific view is available allowing the sequence of work for a single unit to be examined.
- Automation and optimisation to speed up the process of generating and improving rosters. Automation is included to allow the user to quickly find a valid roster plan, or to complete an unfinished one. An optional interface is available allowing an external optimisation tool to control all aspects of a vehicle roster so that an optimal solution is found respecting vehicle movements, empty runs, maintenance activities and any user specific business rules that must be respected.
- The sequence of vehicles within a multiple unit is automatically managed in Viriato. Thus the rostering tool determines when a vehicle has changed direction, and alerts the user if a roster plan contains planned activities which are not possible because a vehicle is trapped by another unit.
- Built in plausibility checks ensure that the rosters created by the user contain links for all dates within the timetable period ensuring the creation of valid rosters.
- Reports showing utilisation of vehicles during each day and vehicles waiting at nodes allowing the planner to manage times of peak demand for rolling stock and storage locations.
- Empty runs for stock balancing purposes can be created as rostering activities. This allows the planner to see the effects on capacity consumption of the vehicle roster to make the roster more reliable.
- Maintenance activities can be planned in the roster, with validation rules based on time interval between activities (e.g. a cleaning activity every four hours) or distance between activities (e.g. refuelling at least every 1000km). Rule sets can be defined specifying which types of activities can occur at each location, allowing flexible planning of vehicle specific tasks.
Keeping track
Platform occupancy
Stations are at the heart of railway operations. Here lines converge, trains arrive and depart, passengers come and go and change trains, and trains are taken out of service, cleaned and maintained. As train operators introduce regular interval timetables and develop major connection points, the operational functions and capacity requirements placed on stations increase significantly.
Given these conditions, every step must be planned in detail. Therefore the analysis of arrival/departure times, the allocation of platforms and their occupancy is a core part of the timetable production process. The questions that are addressed in this analysis include: Are there sufficient platforms available for the proposed service concept? And what additional tracks or switches are needed to increase the service?
Viriato’s platform occupancy module provides timetable planners with a simple and powerful tool for planning, evaluating and producing platform occupation charts. The planner can drag and drop trains between platforms and review conflicting moves instantly.
Viriato can help the timetable planner to create conflict-free platform workings with the optional conflict detection module displaying planning rule violations and conflicts between services on a given track or between arriving and departing trains from different tracks within the station area.
The dark side of capacity
Conflict detection
A railway timetable is subject to numerous constraints, including those due to infrastructure (line headways, interlocking systems, etc.), vehicles (performance, train type, etc.) and the service pattern (intermediate stops, connections, etc.). The higher the railway system’s degree of complexity, and the closer to operating at design capacity, the more these constraints must be considered in timetable planning.
In complex cases it can be very difficult to verify that all the constraints on operation have been considered and that the proposed timetable remains conflict-free.
Viriato’s conflict detection module rapidly determines and visualises all conflicts on the graphic timetable. The user can alter a planned train by dragging the path on the graphic timetable, and any remaining conflicts are instantly shown. Viriato produces a tabular summary of conflicts and durations to enable the planner to resolve them quickly.
The Viriato conflict detection module also detects platform allocation issues. Our rigorous mathematical algorithm detects conflicts within a platform occupation plan, and alerts the user if the proposed service pattern is infeasible, providing a valuable early warning to the train planner.
Getting there
Trip time analysis
Timetable production is an interactive process involving many constraints and conflicting goals. Operational constraints often have impacts that are not initially obvious. Furthermore, the system-wide impacts of local timetable changes are not directly evident in large railway networks.
Viriato’s trip time analysis module enables timetable planners to compare alternative timetables and analyse timetable and service quality. It starts by identifying all meaningful connections based on the timetable data, trip times and user-defined transfer times. Once the connections have been identified, Viriato calculates the alternative’s most important customer and operational qualities.
The trip time analysis module provides many different analysis tools enabling timetable planners to thoroughly evaluate alternative timetables, and permitting the attractive presentation of this data in a variety of graphical formats. This allows the travel opportunities offered by the new timetable to the railway and its customers to be communicated effectively.
Understanding passenger flows
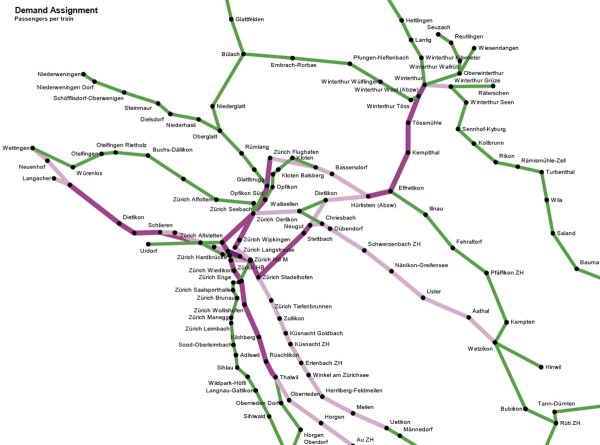
Demand assignment
The creation of a new timetable and service often influences the choice of route taken by passengers. The Viriato add-on module trip time analysis calculates the routes that can be taken by passengers, including changing trains and indicates any change of service quality between timetables. The Demand Assignment module goes one step further, as it incorporates the passenger demand into trip time analysis and thus allows the determination of the number of passengers travelling on each train in the timetable.
An iterative process is carried out within Viriato which makes transparent to the user the interaction between new timetable service concepts and the associated changes in passenger routing and flows. Within this process occurs the timetable concept creation itself, calculation of the possible connections available, apportionment of the passenger demand on the new routes and thus the loading of trains. As the user modifies the timetable concept this process repeats. This analysis is all undertaken within Viriato using the Trip Time Analysis and Demand Assignment add-on modules.
The algorithm for passenger assignment uses an analogy with the flow of electrical current based on the principle of simultaneous apportionment to calculate routing and loads. The demand from every origin-destination pair is simultaneously distributed to trains based on the relative “resistance” experienced for each choice, i.e. the attractiveness to passengers of each possible journey is calculated based on the travel time and number of connections required.
Viriato also calculates the distribution curves containing the fraction of passengers who wish to travel each hour used by the module based on known travel patterns between locations, allowing the modelling of morning and evening peaks, flows into major conurbations, etc.
Dealing with uncertainty
Robustness analysis
In the iterative process of timetable production, evaluation of plans plays an important role. One aspect which is usually especially hard to quantify and assess is the operational robustness of a timetable variant. The determination of the impact of local infrastructure or timetable changes on the robustness of the whole system is a difficult task even for experienced planners when working with large networks.
The robustness analysis module allows the validation of the stability of a timetable and the comparison of the performance of alternative timetables. The user develops delay scenarios containing a set of pre-defined incidents that they wish to test a timetable against. This is then processed by Viriato using the infrastructure data, with the original delays propagated through the timetable until the service pattern returns to normal. Once the calculation is done Viriato produces statistics and the perturbed timetable can be saved as a regular Viriato scenario.
The result of the delay propagation may be reviewed using Viriato, and includes statistics such as the duration for recovery and the total delay minutes due to the original perturbation. These statistics can be exported and used for further analysis and for the presentation of results. Results saved in a new timetable scenario can be displayed and analysed using all the standard Viriato functions. This allows the robustness of any new timetable to be effectively analysed and easily communicated.
Keeping the railway running
Works planning
Although the key reason for running a railway is moving passengers and goods, it should not be forgotten that there is the requirement to maintain and upgrade the infrastructure to allow operations to continue and grow. Without maintenance work, the condition of railway assets soon begins to degrade.
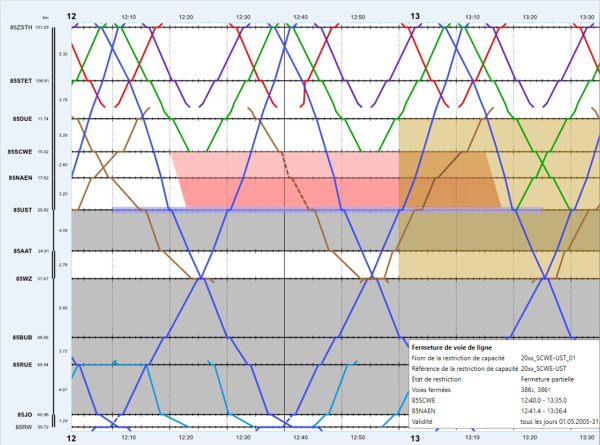
While Infrastructure Managers try to minimise the effects of these engineering works on their customers, they often have consequences to planned trains which may require modification to allow them to run on days with works. Train operators need to know which tracks are available between stations, within stations them selves, and will there be any additional running time due to speed restrictions?
The works planning module allows the creation of the engineering works, and the display of the interactions with planned trains. The engineering works can be collected together through the use of scenarios, allowing the user to group and filter subsets of the works based on their own criterion.
The engineering works can be visualised in the graphic timetable within Viriato, allowing an immediate overview of trains which are planned to run through track sections which are closed, or have a speed restriction planned. A report can be created that shows in detail exactly which trains are affected on each date during the timetable period, allowing them to be identified and replanned for the affected dates.
To allow the user to take a more strategic view of the engineering works, a second visualisation of the data in Viriato has also been developed which shows a summarised view of the works on a day-by-day basis. For each section in the network, the restriction is summarised as being full or partial and day and/or night. This view allows the user to quickly identify the pattern of restrictions, to check whether alternative routes are available and to make decisions regarding their train timetable.
Taking platform thinking further
Interfaces
A train timetable goes through many planning stages over its long period of development. The process starts with the preparation of a draft service plan. This is constantly refined until operations of the train commence. Finally, after the introduction of the timetable system performance is analysed. Finding the timetable that best balances the railway’s operational and economic needs requires much iteration.
Viriato’s versatility enables it to support timetable planners at all stages of the development process. Nevertheless data will almost certainly need to be exchanged with other applications at some point in the process, and used either in parallel or sequentially. A central element in the data exchange process is insuring efficient data flow without wasteful and error-prone re-collection of data. The challenge consists of linking different applications over intelligent and standardised interfaces.
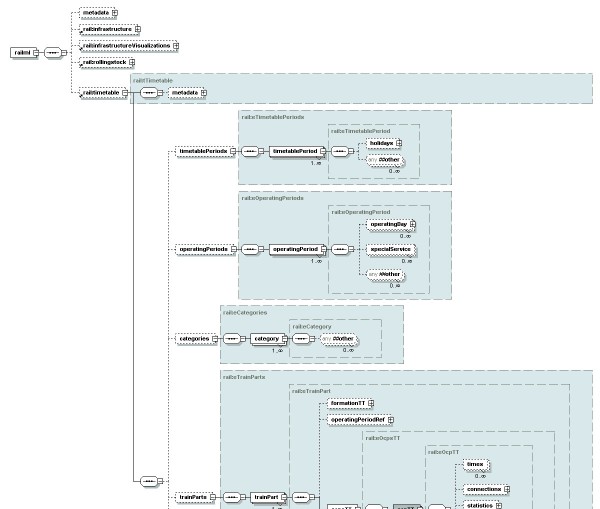
The railML initiative was created to improve the data exchange process between railway information technology applications (www.railML.org) through the development of agreed standards. SMA und Partner AG was a founding member of the railML initiative and continues to actively participate in railML development. The goal of railML is to link different applications through the creation of defined interfaces between diverse rail service planning and operations IT applications, and to simplify information exchange with the definition of standardised XML-based schemas.